Transforming PDF Content into Interactive Q&A with RAG and Vector Databases
Utilizing Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), vector databases, and a Language Model (LLM) to deliver accurate answers to user queries extracted directly from PDF files.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The Problem
- The Solution
- How It Works
- Addressing Key Challenges and Potential Enhancements
- Conclusion
Introduction
In today's fast-paced digital world, accessing relevant information quickly and efficiently is paramount. Traditional search methods often fall short, especially when dealing with large documents like PDFs. To address this challenge, I developed an application that leverages Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), vector databases, and a Language Model (LLM) to provide users with precise answers to their questions directly from PDF files.
The Problem
PDF files are widely used across industries for documentation, reports, and research papers. However, efficiently extracting precise information from these documents poses challenges. Traditional keyword-based search methods often yield irrelevant results, necessitating users to manually sift through extensive text, which is both time-consuming and inefficient.
The Solution
My app addresses this problem by integrating new technologies such as:
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Combines retrieval-based methods with generative models to provide accurate and contextually relevant answers.
- Vector Databases: Store document data in a format that facilitates efficient similarity search, enabling quick retrieval of relevant passages.
- Language Model (LLM): Processes the retrieved information to generate coherent and accurate responses to user queries.
How It Works
Step 1: PDF Ingestion
The first step involves uploading the PDF file into the system. The document is parsed, and its content is divided into manageable chunks. Each chunk is then embedded into a vector space using the OpenAI Embeddings API, capturing the semantic meaning of the text.
Step 2: Vector Storage
The vector representations of the document chunks are stored in a vector database powered by Pinecone. This database allows for efficient similarity searches, enabling the system to quickly locate the most relevant chunks of text in response to a user query.
Step 3: Query Processing
When a user submits a question, it is also converted into a vector representation. This vector is then used to search the Pinecone vector database for the most semantically similar document chunks.
Step 4: Answer Generation
The retrieved chunks are fed into the Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3 language model from the Hugging Face API, which generates a coherent and contextually accurate answer based on the information from the document. This ensures that the response is not only relevant but also easy to understand.
Langchain Integration
I used Langchain to seamlessly integrate all these technologies, enabling efficient communication between the different components and ensuring smooth operation of the entire system.
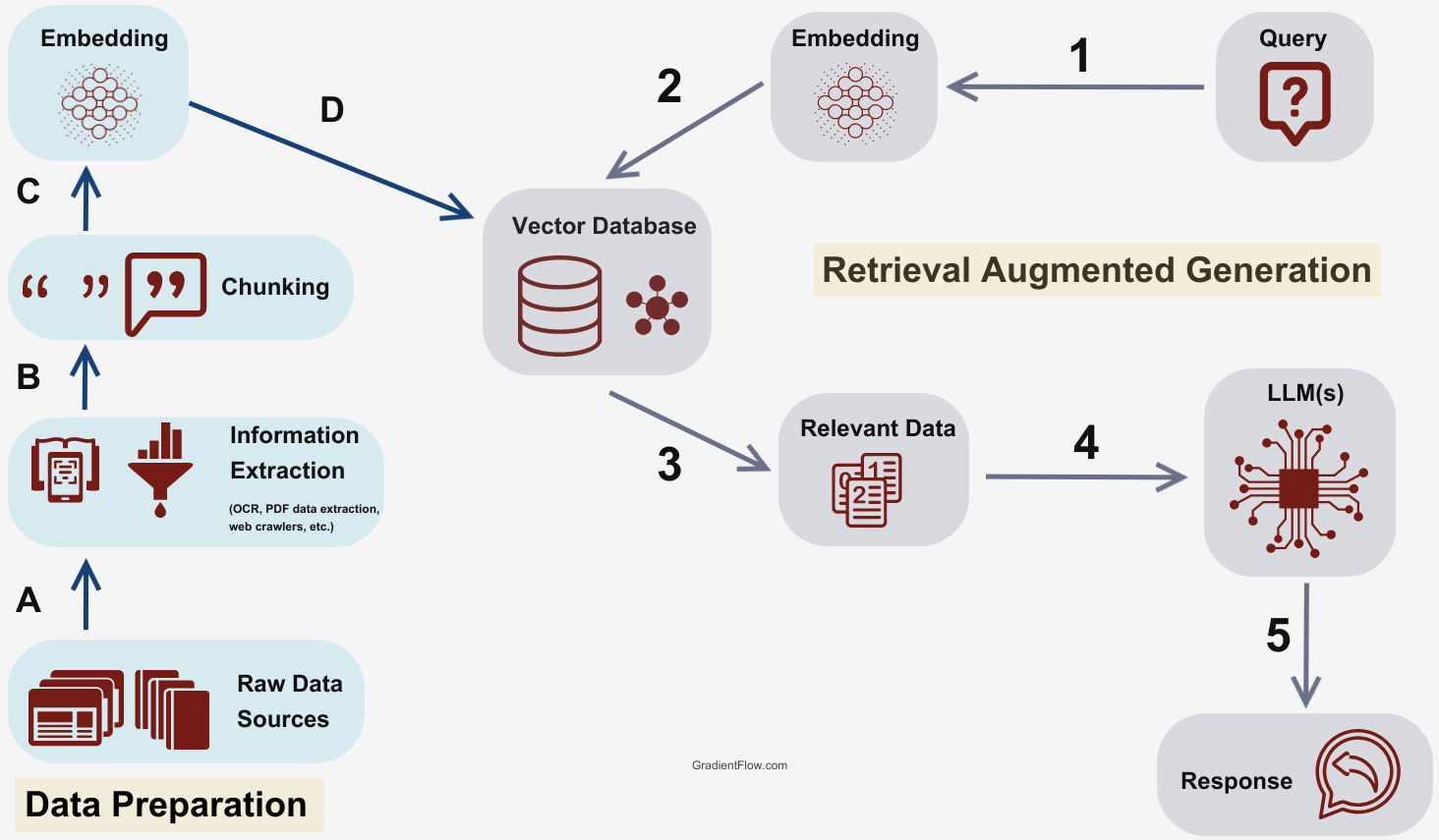
Figure: Visualization of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Process
Addressing Key Challenges and Potential Enhancements
Challenge 1: Handling Random Text Inputs
When a user inputs random text, the application may still attempt to provide a response. This can lead to irrelevant or incorrect answers, undermining the user experience and utility of the application.
Potential solution: Implement a robust input validation mechanism that assesses the relevance and context of user queries before processing them. Utilize techniques such as natural language understanding (NLU) to filter out nonsensical or unrelated queries. Additionally, clearly communicate to users when their input does not align with the expected query format or context.
Challenge 2: Language Model (LLM) Response Language Discrepancy
The language model occasionally responds in a different language than the one used in the question. This mismatch can confuse users and reduce the clarity and effectiveness of the application's responses.
Potential solution: Introduce language detection capabilities to identify the language of incoming queries. Ensure that the LLM is configured to respond in the same language as the query whenever possible. Implement language-specific models or translation services to facilitate accurate and coherent responses across different languages.
Additional Enhancements
- Fallback Mechanism: Develop a fallback strategy for scenarios where the system cannot confidently generate a response. This could involve informing the user about the limitation and suggesting alternative means to obtain the information.
- User Feedback Loop: Implement mechanisms for users to provide feedback on the accuracy and relevance of responses. Use this feedback to continuously refine and improve the model's performance through iterative updates and training.
By addressing these issues through systematic enhancements and improvements in model handling and user interaction, the application can significantly enhance its reliability and usability, providing more accurate and contextually appropriate responses to user queries.
Conclusion
By leveraging RAG, vector databases, and advanced language models, my application transforms static PDF content into an interactive Q&A experience. This innovation not only saves users time but also enhances their ability to access and utilize information effectively.
Project Links
- GitHub Repository: Link to GitHub Repo
- Project Preview: Link to Project Preview